During a routine physical exam, your physician may discover an enlarged or swollen vein in the scrotum, a condition known as varicocele. It isn’t always accompanied by symptoms, but it can be painful and affect sperm quality. Fortunately, varicocele treatment is a viable option. The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis. Usually, the doctor will need to perform a scrotal ultrasound to diagnose a varicocele, and treatment can be performed at the same time.
The most common procedure for varicocele treatment is the subinguinal varicocelectomy, which is performed through an incision on the groin. It is a relatively safe procedure, and most men are able to go home the same day. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The procedure involves making an incision on one side of the penis and tying off the veins. A small dressing is applied afterwards.
Another type of treatment involves percutaneous embolization. This procedure involves the use of a catheter to block a varicocele vein. This method is performed as an outpatient procedure, and patients are able to return to normal activities the next day. Percutaneous embolization is performed by interventional radiologists, who are trained in minimally invasive techniques. Using x-ray imaging, the doctor inserts a tube into a varicocele vein. The radiologist then injects a solution that makes the vein block. The solution causes scarring, but the vein can still exit the body through normal pathways.
Varicocele is often discovered during fertility evaluations. The valves that are in the spermatic cord carry blood to the testicle, and if the valves are faulty, blood can flow through the varicocele instead. The valves stop working correctly, and the blood pooling in the veins causes the vessels to dilate. This results in higher scrotum temperature, which can affect sperm production.
If the testicle is enlarged, the condition can be treated through a procedure called microscopic varicocelectomy. This method involves making an incision in the groin, which is usually about two to three inches in length. During the procedure, the surgeon ligates several tiny veins. The procedure generally lasts for two to three hours.
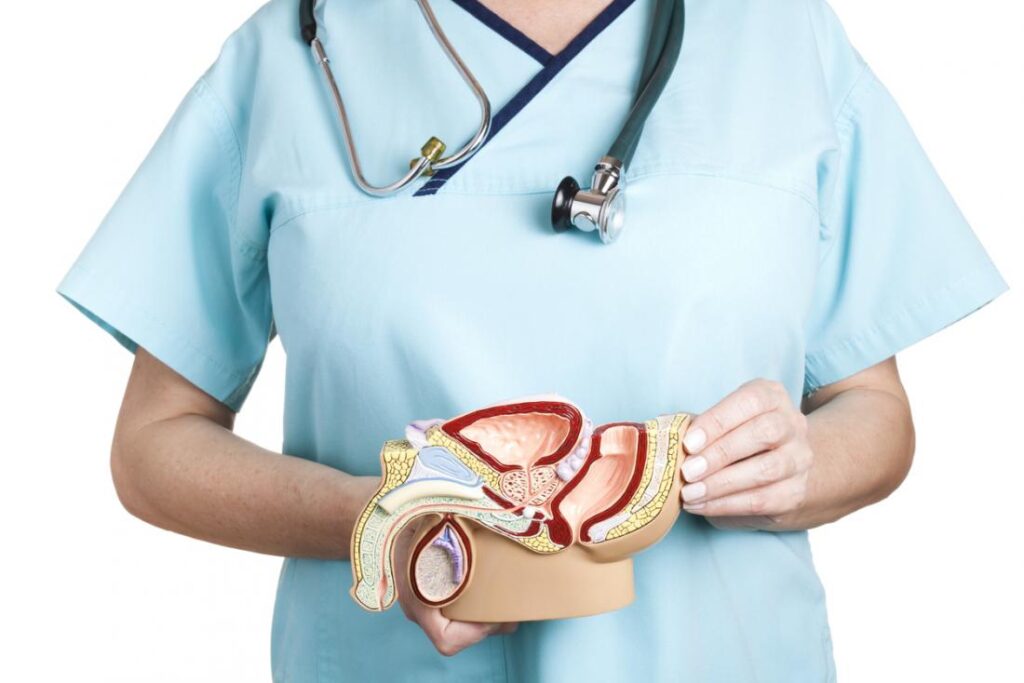
There are other varicocele treatment methods, which involve tying off the veins, or performing a surgery. A surgery is generally considered necessary only if the testicle is significantly atrophying or if the pain is severe. It is also important to remember that varicoceles are usually harmless, but in some cases, they can become infected and result in serious complications.
Varicocele treatment can also improve the quality of sperm in infertile men. The procedure is a relatively simple and minimally invasive procedure, which can help improve the quality of sperm and the amount of semen produced. It also helps the patient get back to normal activity quickly, since the surgery requires a short recovery period. The patient can return to work the next day, and can usually go back to normal activities in about a week.
Varicocele treatment should not be performed for at least 10 days after the procedure. During this time, the patient should not participate in activities that require physical exertion, such as running or jumping.