Several different medical conditions can cause blood to be present in your urine. Infection, glomerulonephritis, kidney stones, bladder cancer, and urinary tract tumors are just a few of the causes of blood in urine. While hematuria is not a dangerous condition, it should be treated as soon as possible. A delay in treatment may cause serious health complications, such as kidney failure.
When hematuria is caused by an infection, it will be treated with antibiotics. The doctor will take a urine sample and perform a test to find out if the infection is present. Your healthcare provider will also perform a physical exam. He or she will check your lower abdomen and flanks, as well as your pelvic area. He or she will ask you about any symptoms that may have occurred, and ask about your medical history.
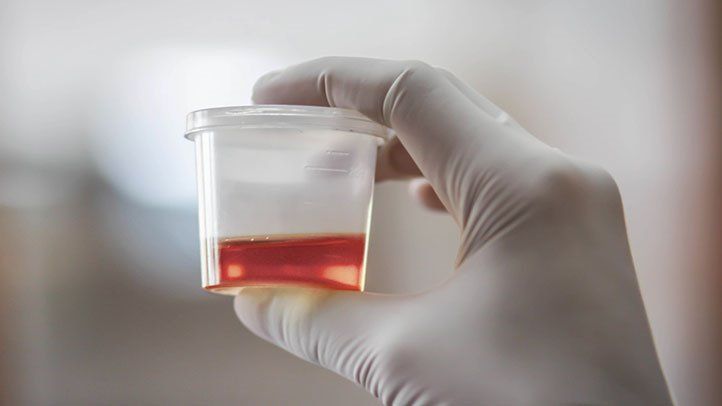
Urinary tract infections are the most common causes of hematuria, but there are several other conditions that can also lead to blood in the urine. Symptoms can include urinary frequency, abdominal pain, and pain in the back or lower abdomen. Blood in the urine can be a sign of a serious health problem, such as kidney disease or prostate cancer.
Urinary tract tumors are also a very serious medical condition, and if left untreated, they can cause serious damage to the bladder or kidneys. The most common type of urinary tract tumor is bladder cancer. Cigarette smoking is a major risk factor for bladder cancer.
Other conditions that can lead to hematuria include bleeding disorders, enlarged prostate, and urinary tract tumors. Although most people with hematuria recover on their own, a severe form of hematuria can cause chronic kidney failure, and requires treatment. A symptomatic hematuria that requires treatment may include symptom management, surgery, or antibiotics.
Some medications can also cause blood in the urine. The blood can be either visible or microscopic. The doctor may take a urine sample and run a test to find out if the cause of the hematuria is an infection or a medication.
A physical exam can help to determine if hematuria is caused by kidney disease. Your doctor will ask you about your medical history, including past injuries and conditions. He or she will also ask you about any medications that you are taking. Your doctor will look for any signs of injury, including bruises, punctures, swelling, or wounds.
A kidney biopsy may be performed to diagnose hematuria. A biopsy involves taking a small piece of tissue from the kidney. The pathologist will then analyze the tissue in the lab. If the cause is a disease, your doctor will order imaging tests. In some cases, your doctor may also order blood tests to check for autoimmune diseases, kidney stones, and prostate cancer.
If you have blood in your urine, you should be tested immediately. This can help to diagnose hematuria and help to prevent serious complications from occurring. Your doctor will also give you light sedation if necessary.