Whether you’ve just found blood in your urine or have been experiencing the symptoms for a while, you should see a doctor for treatment. This condition is not usually life-threatening, but it can be a sign of an underlying health problem. It can also increase your risk of developing cancer.
The causes of blood in urine are often unknown. However, there are some common causes, including infection, medications, or chronic disease. For example, blood can be caused by a urinary tract infection. This is usually caused by cystitis, a condition in which bacteria enter the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body. Usually, a urinary catheter is used to help drain urine from the bladder. If you have this type of device, you may be able to have a hematuria test. This test can help identify any infections in the urinary tract.
In addition to urinary tract infections, there are a few other reasons why you might have blood in your urine. For instance, if you are using an anti-cancer drug called cyclophosphamide, it can cause urinary bleeding. This can also occur if you are using penicillin or other antibiotics. Alternatively, you might have an enlarged prostate gland, which can make it difficult to urinate. It is important to discuss your medical history with your provider, as some conditions can affect the amount of blood that comes out of your system.
Urine that has blood in it may be pink, red, or even smoky brown. Sometimes, blood can be present in tiny blood clots. This is a symptom of an underlying condition, and the doctor may recommend that you see a urologist.
The doctor may ask you to fast before testing. You should also inform your provider about any menstrual periods you have. It is also important to tell your provider if you have hemorrhoids. This is because hemorrhoids bleed easily. If you have hemorrhoids, you may be able to have hematuria test without any special preparation. You should disclose to your provider any hemorrhoidal conditions you may have, as it will affect the test results.
Depending on your age, the doctor may order imaging tests. This includes ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography (CT). These tests can help detect blockages in the urinary tract and other medical conditions. You may also have a cystoscopy, which is a type of examination of the bladder and kidneys. This examination is usually performed in people over the age of 50, but you may also need this test if you are younger.
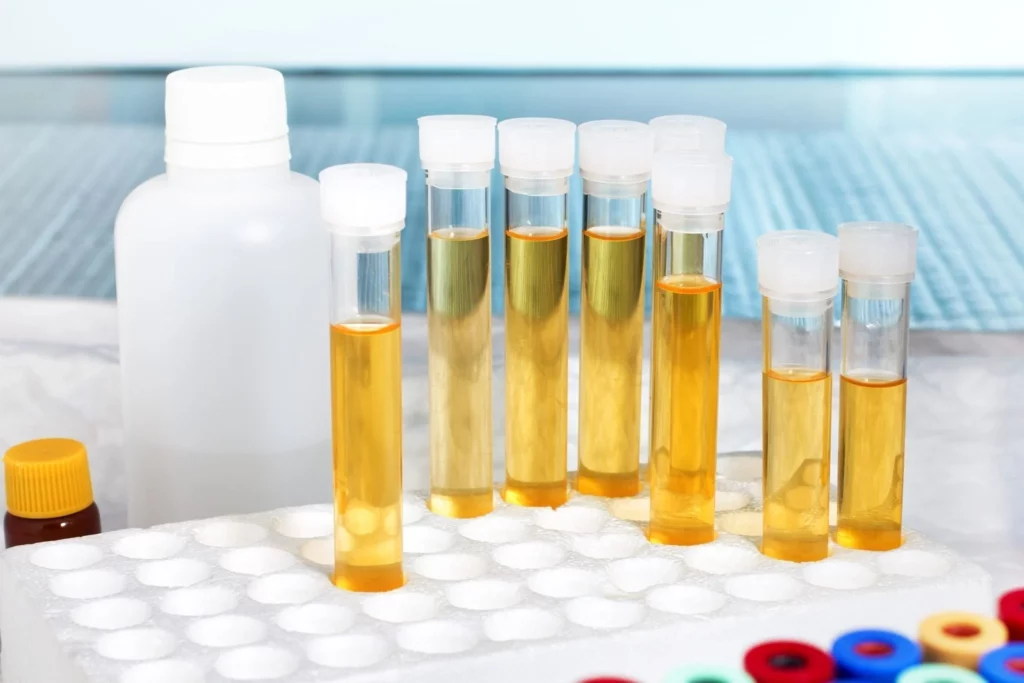

Your doctor can also do a urine test to identify blood in your urine. This is usually a part of a routine urinalysis. The test will help your doctor find out whether there are red blood cells or other substances in your urine. You may have to repeat the test after treatment to check for blood again.
Your doctor will ask questions about your medical history and symptoms. If you have a history of cancer or other serious conditions, this can increase your risk of developing blood in urine. It is important to rule out a cancer or other serious illness as soon as possible. You may also need to undergo a kidney biopsy, which is a procedure that will help your doctor determine the cause of blood in your urine.